Common Mineral Exploration Terminology
Mineral exploration companies employ various terms to describe mineral deposits and the form and character of mineralization. Below are some key terms:
Alteration
Refers to the modification in the minerals or chemical composition of the country or host rock, caused by chemical reactions with hydrothermal solutions. Mining company updates may refer to the discovery of an “alteration zone”. These alteration zones are commonly associated with, and surround, many mineral deposits. The significance of identifying an alteration zone lies in its potential indication of a nearby hydrothermal mineral deposit.
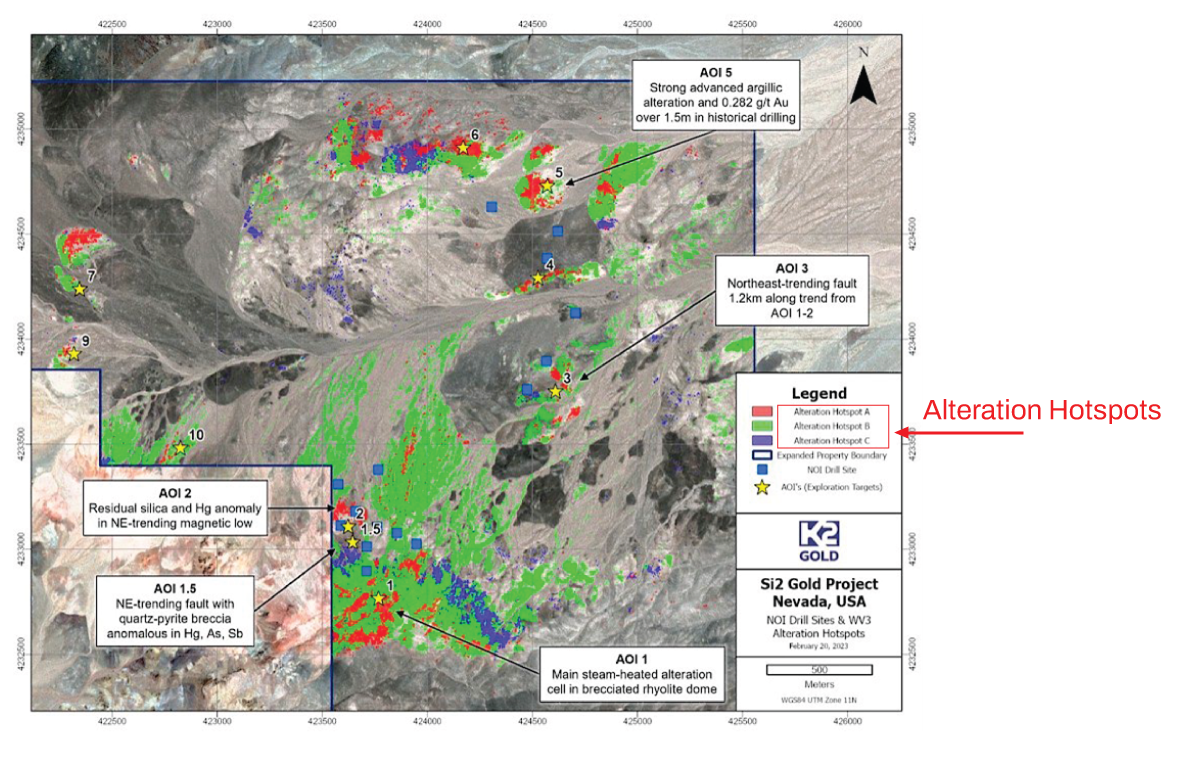
Image 1: Location of key targets (Area of Interest – AOI) and drill sites planned at Si2 project. (K2 Gold, May 2, 2023).
Grade
Refers to the concentration of individual ore metals within a rock sample, typically expressed as a weight percentage. Most metals are reported in percent (%), except for gold (Au), Silver (Ag), platinum (Pt), and palladium (Pd), which are reported in grams per tonne (g/t) or ounces per ton (opt) due to their low concentrations. Common units are:
- ppm = parts per million
- ppb = parts per billion
- % = percent or part per hundred
- g/t = grams per tonne (also equal to a part per million)
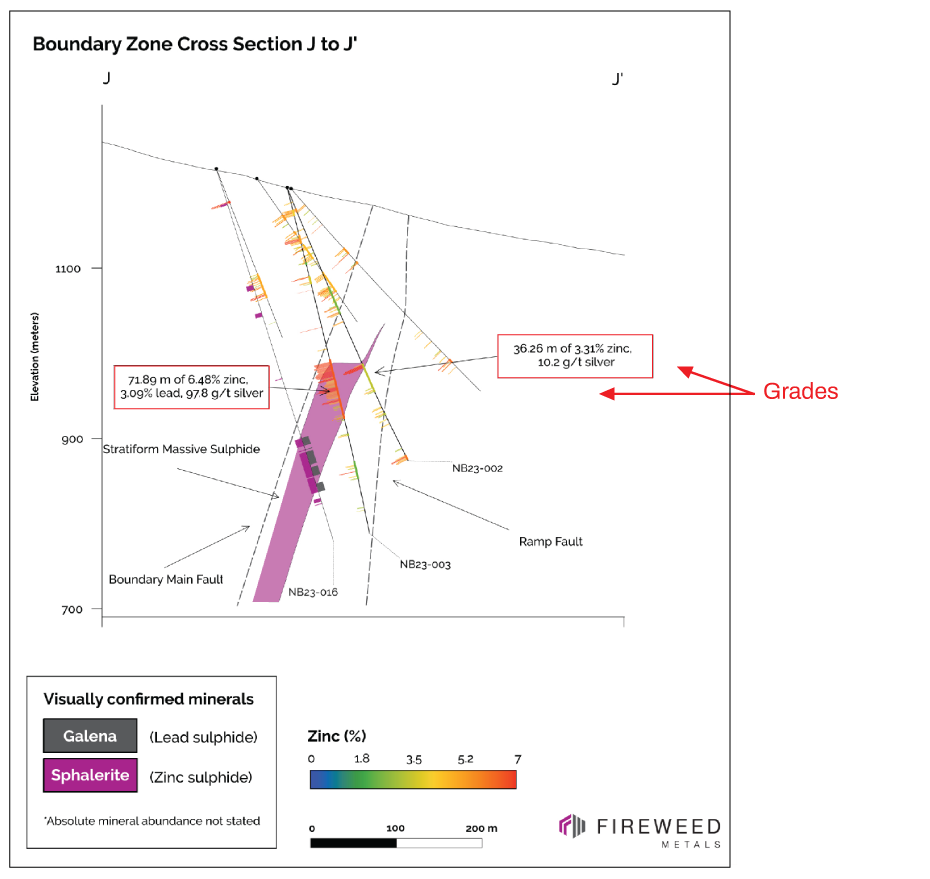
Image 2: Cross Section J-J’ Wide intersection of massive sulphides steps-out the stratiform mineralized zone down-dip with high grades in NB23-003, and a wide interval in NB23-016. Preliminary interpretation of the approximate shape of the stratiform mineralized zone shown in purple. (Fireweed Metals, July 26, 2023).
Mineralization
Broad term used to describe a “rock of potential interest.” It typically refers to an area containing potentially economic minerals or displaying characteristics that suggest the presence of economic minerals.
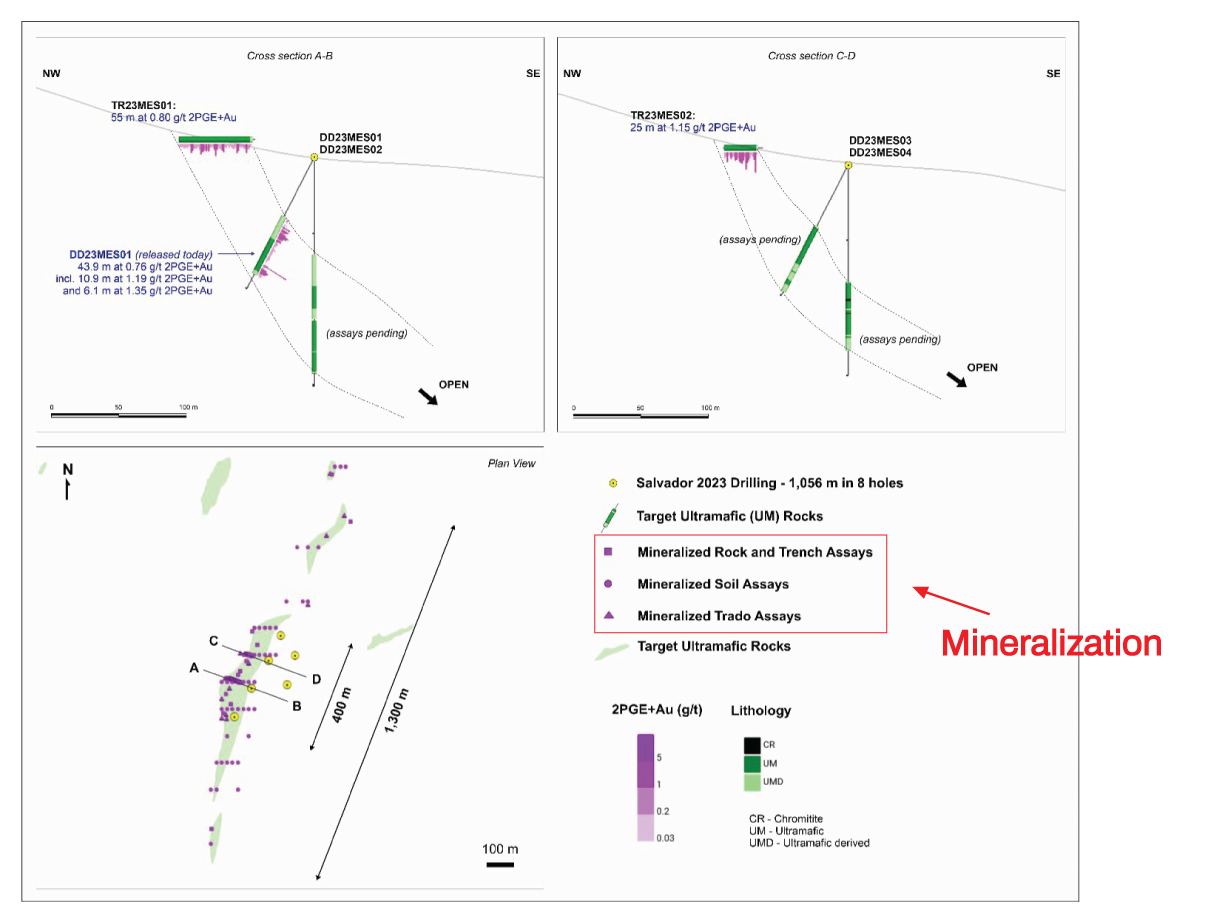
Image 3: Cross sections along the main zone at the Salvador target at ValOre Metals’ Pedra Branca PGE Project.
(ValOre Metals, October 4, 2023).
Mineral Deposit
Naturally occurring body of rock that hosts an anomalous concentration of potentially valuable mineral(s) or elements which can potentially be extracted at a profit. A body of rocks should only be called a mineral deposit if it is reasonable, but not yet proven, that it could be mined with existing technology and feasible metal prices.

Image 4: Trapiá 1 Deposit long section (looking NE) highlighting location of drill hole DD23TU33 and the 300 m step out drilling at DD23TU32. (ValOre Metals, September 25, 2023).
Ore Deposit
An ore deposit is a mineral deposit that has been proven to be economically viable through engineering and economic analysis. A rock body should only be called an ore deposit or ore if it is actively being mined, or has mineral reserves defined in a pre-feasibility or feasibility study
Prospect and Showing
Terms used to describe an area of mineralization where a mineral deposit or resource estimate has not yet been defined.
Understanding terms such as alteration, grade, mineralization, mineral deposit, ore deposit, prospect and showing is essential for geologists, mineral exploration and mining companies, and investors to effectively communicate and assess the potential of various projects.

