Great Bear Discovers New High-Grade “Yuma” Zone at 1.4 km Step-Out Along LP Fault from the Bear-Rimini Zone in Unassayed Historical Drill Core: Follow-Up Drill Results Pending
July 16, 2019 – Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada – Great Bear Resources Ltd. (the "Company" or "Great Bear", TSX-V: GBR) today reported the discovery of the new high-grade “Yuma” gold zone at its 100% owned Dixie Project in the Red Lake District of Ontario.
Like the recently discovered Bear-Rimini Zone (see news release of May 28, 2019), the Yuma Zone is also hosted by the “LP Fault”, which is an 18 kilometre long gold-bearing deep-seated crustal structure at the Dixie project. Both new high-grade gold zones within the LP Fault are shown in Figure 1.
Highlights of the new Yuma gold discovery include:
- Historic drill hole DC-12-07 (drilled in 2007 by past operators) is a 1.4 kilometre step-out to the southeast along the LP Fault from Great Bear’s Bear-Rimini discovery hole DNW-011, and was the only other hole to be drilled to-date into the footwall of the LP Fault.
- The final metres of DC-12-07 intersected silicified volcanic rocks visibly similar to those which yielded high-grade gold at the Bear-Rimini discovery. Lower-grade gold mineralization was also intersected higher up the hole within the LP Fault, as was also the case in the Bear-Rimini Zone.
- Great Bear’s geologists noted sparse fine visible gold within strongly silicified felsic volcanic rocks towards the end of DC-12-07, where the Company projected the Bear-Rimini Zone’s on-strike gold mineralization could occur. Past operators had recorded this interval as un-mineralized and it had not been sampled.
- Great Bear sampled the previously uncut core, which assayed 5.5 metres of 4.07 g/t gold beginning at 193.50 metres down-hole, including 2.0 metres of 10.57 g/t gold and including 0.5 metres of 36.90 g/t gold. The historical hole had been terminated prematurely.
- Two historical drill holes were subsequently re-entered and extended by Great Bear, as shown on Figure 2. Both holes intersected similar silicified geology to drill hole DC-12-07 and assays are pending.
Chris Taylor, President and CEO of Great Bear said, “This is the cheapest discovery hole we’ve ever had, since the high-grade visible gold interval was sitting unreported for 12 years in drill core stored on the property. The new Yuma zone matched our projections of where a Bear-Rimini type gold zone could exist along strike and flanking the LP Fault. We now know that high-grade gold is present in both locations where the footwall of the fault has been drilled across 1.4 kilometres of strike length, however the majority of the fault’s 18 kilometres of projected strike length remain untested. We plan to complete further step-outs along the LP Fault and the parallel North Fault to see just how extensive this system is, and how it varies in gold distribution.”
The company has fast-tracked re-logging and sampling of all available historical drill core from areas north of the LP Fault zone. Results will be released as received and analyzed. Follow-up drilling is already underway.
Figure 1: Map zoomed into approximately 5 kilometres strike length of the LP Fault at Dixie, showing the Bear-Rimini and Yuma Zones. The location of the nearby Dixie Limb and Hinge Zones are also shown.
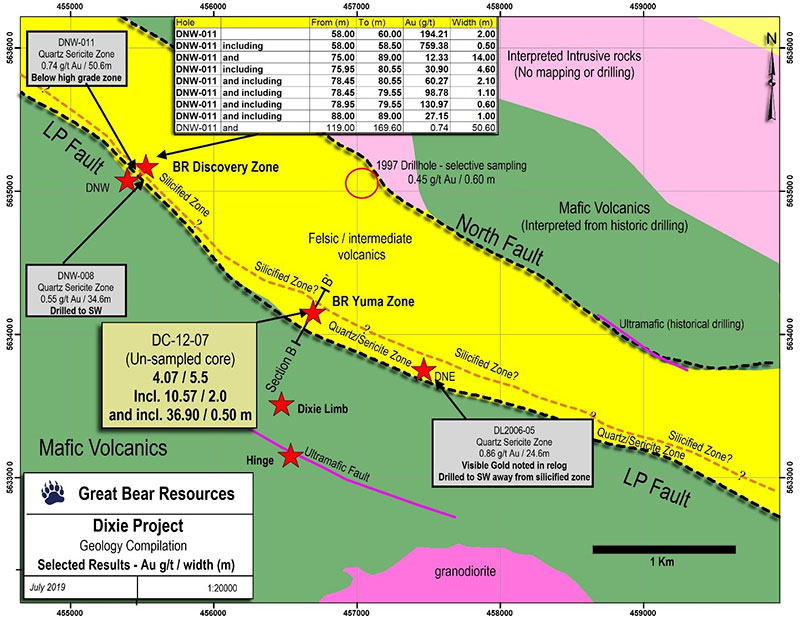
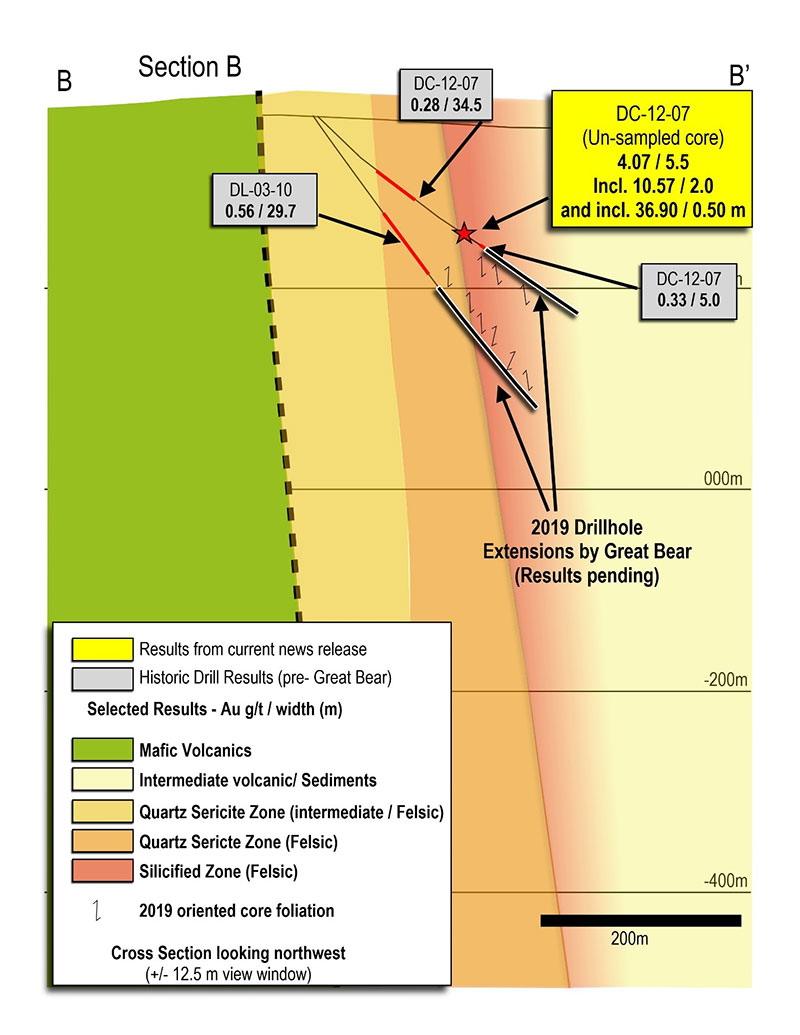
Figure 2: Cross section B - B’ (section location shown on Figure 1) of the Yuma Zone, showing assay intervals and the location of Great Bear’s drill hole extensions.
Drill Hole DC-12-07 (Yuma Zone) Description
Reglogging of hole DC-12-07 identified quartz-sericite-pyrite altered intermediate to felsic volcanic rocks. Historical sampling had outlined two low grade zones of gold mineralization (0.28 g/t gold over 34.5 metres and 0.33 g/t gold over 5.0 metres, shown visually on Figure 2) higher up the drill hole and associated with the LP Fault; the drill hole’s deepest reported assay interval was 1.03 g/t gold over 0.5 metres at 218.25 metres depth. A zone of strong silicification with visible gold was noted near the bottom of the hole from 193.50 metres to 199.00 metres in unsampled drill core, shown in Figure 3. For comparison, the lower image in Figure 3 shows drill core from Great Bear’s Bear-Rimini discovery hole DNW-011, located 1.4 kilometres away. Zones in both holes are hosted within similar felsic volcanic host rocks, both have widespread quartz-sericite-pyrite alteration and the high-grade gold in both holes is hosted by strong silicification.
Figure 3: Images comparing geology, alteration and visible gold mineralization at the new, historically unassayed Yuma Zone (above) and the Bear-Rimini Zone drilled by Great Bear (below). Both zones occur 1.4 kilometres apart along the LP Fault in similar host rocks.

Extension of Historical Holes
DC-12-07 has now been re-entered and extended by Great Bear from its original 218.25 metre length to 336 metres. Oriented foliation and quartz vein data suggest that the zone may be dipping steeply to the north. To test this interpretation, historical hole DL-03-10, which was completed by past operators below DC-12-07 at a steeper angle, was also extended from 207 metres to 376.5 metres (as shown in Figure 2). The extension was designed to target the down-dip projection of the observed mineralization in DC-12-07. Both extended drill holes intersected strongly quartz-sericite-pyrite altered felsic volcanic rocks with zones of variable silicification, from which assays are pending. An image of the original on-site core storage is provided in Figure 4.
The Company continues to undertake a fully funded, 90,000 metre drill program that is expected to continue through 2019 and 2020. Targets tested will include the Hinge Zone, Dixie Limb Zone, Bear-Rimini Zone, Yuma Zone, LP Fault, North Fault, and other targets across the property. In order to accelerate the program, a second drill rig was added in February, and a third drill rig arrived in June of 2019. Approximately 55,000 metres of drilling remain in the current program.
With its recently-completed financing, the Company currently has approximately $20,000,000 in cash and no immediate financing requirements.
Figure 4: Cross-stacked historical drill core at the Dixie project. The new Yuma Zone discovery was made when Great Bear sampled previously unrecorded visible gold mineralization in historical drill hole DC-12-07, assaying 2.0 metres of 10.57 g/t gold in the footwall of the LP Fault, 1.4 kilometres southeast of the Bear-Rimini Zone.

About Great Bear
Great Bear Resources Ltd. (TSX-V: GBR) is a well financed company based in Vancouver, Canada, managed by a team with a track record of success in the mineral exploration sector. Great Bear holds a 100% interest, royalty free, in its flagship Dixie property, which is road accessible year-round via Highway 105, a 15 minute drive from downtown Red Lake, Ontario. The Red Lake mining district is one of the premier mining districts in Canada, benefitting from major active mining operations including the Red Lake Gold Mine of Newmont Goldcorp Corp., plus modern infrastructure and a skilled workforce. Production from the Red Lake district does not necessarily reflect the mineralization that may, or may not be hosted on the Company’s Dixie property. The Dixie property covers a drill and geophysically defined multi kilometre gold mineralized structure similar to that associated with other producing gold mines in the district. In addition, Great Bear is also earning a 100% royalty-free interest in the Pakwash, Dedee and Sobel properties, which cover regionally significant gold-controlling structures and prospective geology. All of Great Bear’s Red Lake projects are accessible year-round through existing roads.
Drill core is logged and sampled in a secure core storage facility located in Red Lake Ontario. Core samples from the program are cut in half, using a diamond cutting saw, and are sent to SGS Canada Inc. in Red Lake, Ontario, and Activation Laboratories in Burnaby, British Columbia, both of which are accredited mineral analysis laboratories, for analysis. All samples are analysed for gold using standard Fire Assay-AA techniques. Samples returning over 10.0 g/t gold are analysed utilizing standard Fire Assay-Gravimetric methods. Selected samples with visible gold are also analyzed with a standard 1 kg metallic screen fire assay. Certified gold reference standards, blanks and field duplicates are routinely inserted into the sample stream, as part of Great Bear’s quality control/quality assurance program (QAQC). No QAQC issues were noted with the results reported herein.
Mr. R. Bob Singh, P.Geo, Director and VP Exploration, and Ms. Andrea Diakow P.Geo, Exploration Manager for Great Bear are the Qualified Persons as defined by National Instrument 43-101 responsible for the accuracy of technical information contained in this news release.
For further information please contact Mr. Chris Taylor, P.Geo, President and CEO at 604-646-8354, or Mr. Knox Henderson, Investor Relations, at 604-551-2360.
ON BEHALF OF THE BOARD
“Chris Taylor”
Chris Taylor, President and CEO
Inquiries:
Tel: 604-646-8354
Fax: 604-646-4526
info@greatbearresources.ca
www.greatbearresources.ca
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
This new release may contain forward-looking statements. These statements are based on current expectations and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results could differ materially because of factors discussed in the management discussion and analysis section of our interim and most recent annual financial statement or other reports and filings with the TSX Venture Exchange and applicable Canadian securities regulations. We do not assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements.
We seek safe harbor

